Are your sales teams wasting hours on dead-end leads that should have been screened out months ago?
Is your marketing budget getting flushed down the drain of poor-quality contact details and stale company records?
You are not alone in this.
Recent industry research states that poor data quality is draining businesses an average of $12.9 million per year, with B2B organizations suffering most from their relationship-based, complex sales cycles.
In today’s competitive B2B marketplace, information is not just an asset; it’s the foundation on which all important business decisions are made based on it. Accurate data provides higher email deliverability rates, higher quality leads, decreased sales cycle, and better win rates. Your sales representatives spend less time researching and more time selling, while marketing campaigns provide better targeting and ROI.
Read on and let us help you transform your B2B data quality issues into competitive strengths.
What is B2B Data Quality, and Why Does it Matter
B2B data quality refers to the accuracy, completeness, consistency, and timeliness of information about businesses and their decision-makers stored in systems. Unlike consumer data that typically focuses on individual preferences and behaviors, B2B data focuses on organizational structures, stakeholders, and constantly evolving business relationships.
According to primary research, 87% of respondents indicated that data accuracy is a top challenge in B2B sales prospecting.

High-quality B2B data can include accurate contact information, current job titles and responsibilities, up-to-date company details like revenue and employee count, correct organizational hierarchies, and reliable firmographic data such as industry classifications and technology usage.
The Components of B2B Data Quality
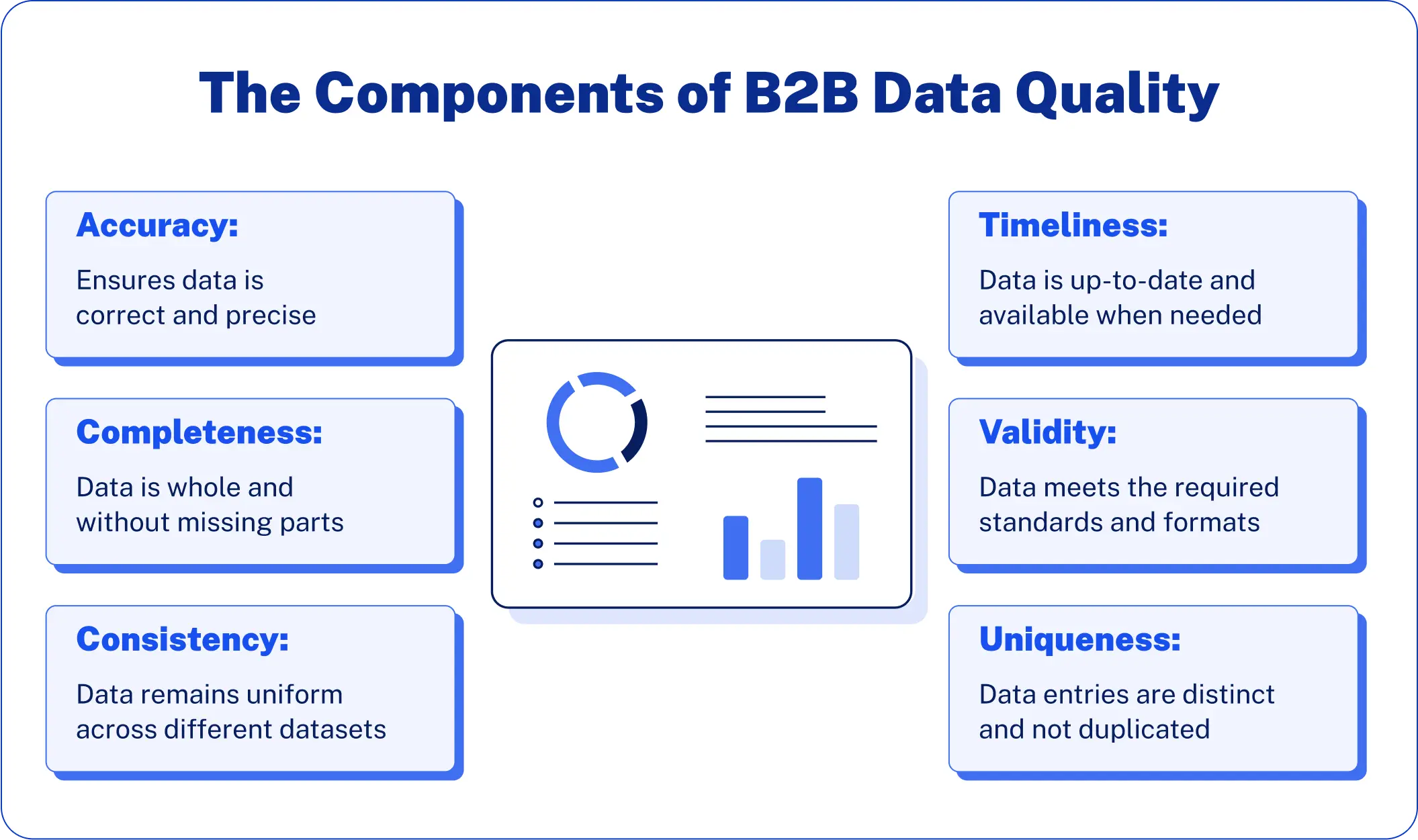
Accuracy ensures that information in your database reflects reality. For example, phone numbers are correct, or business information is current. Inaccurate information creates bounced emails, missed calls, and missed opportunities.
Completeness is the availability of all the required data points needed for effective sales and marketing operations. Complete records not only include primary contact information but also significant contextual information.
Consistency requires uniform formats and repeated data in all systems. The name of the company must use the same naming format, phone numbers must be formatted the same, and data must sync properly between your CRM or other tools.
Timeliness reveals how up-to-date your information is. In today’s fast-changing B2B world, yesterday’s accurate data can become a liability today. People change jobs, companies change hands, and business priorities shift quickly.
Validity confirms data meets the rules and formats that are specified. For example, email addresses have correct syntax, and phone numbers contain correct country codes.
Uniqueness eliminates duplicate records, which can dilute your view of prospects and customers. Multiple entries for the same contact or company create confusion and damage customer experience.
Why B2B Data Quality Matters More Than Ever
The rise of automation and AI in sales and marketing makes data quality even more critical. Automated sequences, predictive analytics, and machine learning models use both good and bad data.
High-quality data enables complex personalizations and intelligent insights, while poor data creates embarrassing mistakes at scale. With data quality impacting 31% of revenue on average according to recent surveys, the correlation between data quality and campaign success has never been clearer.
Your investment in data quality pays off in every aspect of your go-to-market strategy, ranging from first prospecting to customer retention and expansion. When your data foundation is solid, all other initiatives run more effectively and produce better results.
The Data Quality Lifecycle
Learn about the data quality lifecycle to ensure long-term, accurate B2B data. All data follows five stages from acquisition to retirement.
- Collection and Entry begin as soon as data is collected from sources like web forms, events, or purchased lists.
- Validation and Enrichment are verifying accuracy and inputting missing information using email validation and appending information.
- Active Use is the stage of usage, in which data fuels sales activity and campaigns. In this stage, data begins degrading at 2.1% each month.
- Degradation and Decay are unavoidable since individuals switch employers, employers switch, and telephone numbers become outdated.
- Refresh and Renewal completes the task by replacing stale data with new approved data. Organizations with a routine refresh process possess higher-quality data and enhanced campaign effectiveness.
The State of B2B Data Quality Today
B2B data quality today presents a sobering reality: despite increased awareness of its importance, data quality indeed deteriorates in organizations.
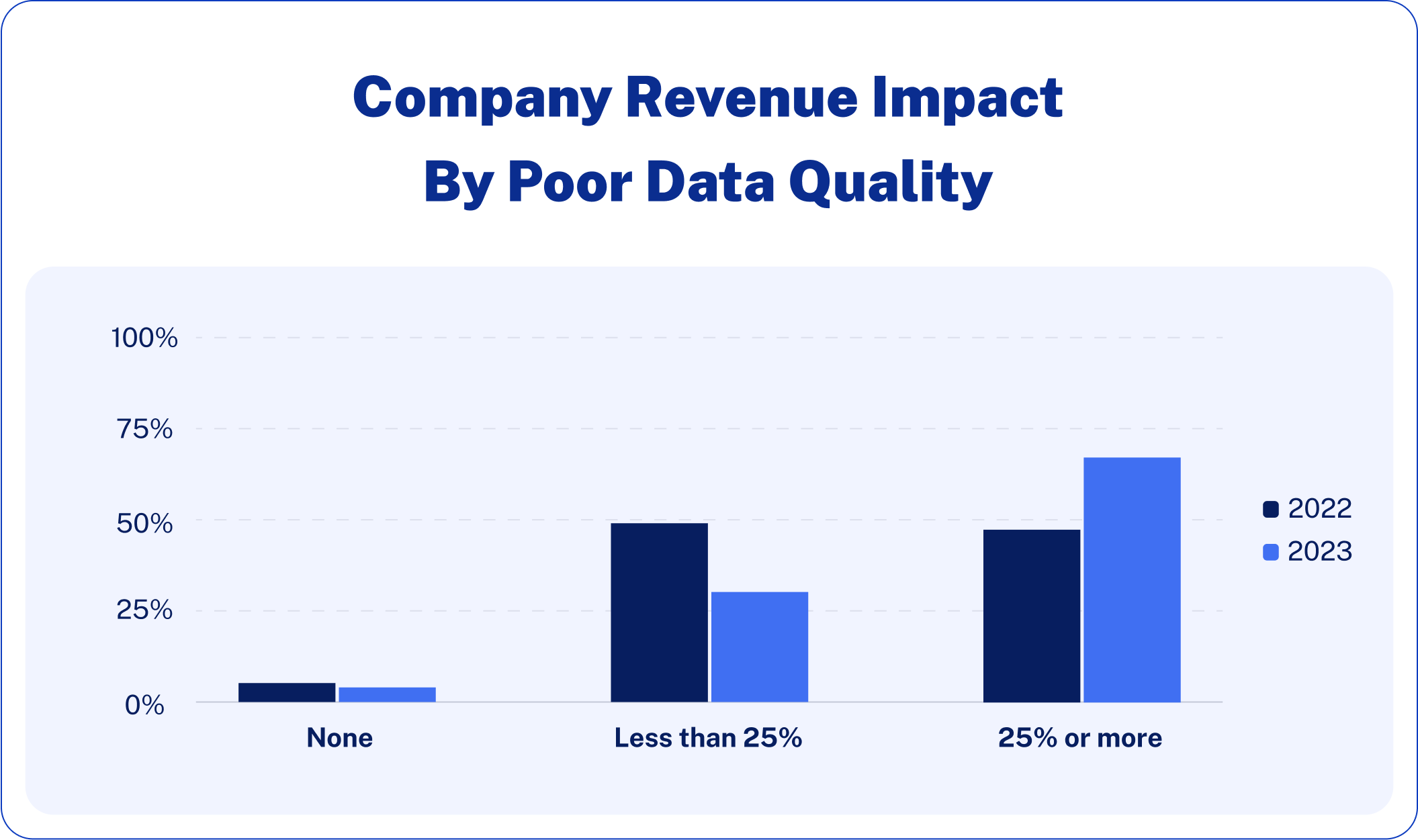
- According to a report in 2024, poor data quality was the number one concern among 456 analytics engineers, data engineers, and data analysts surveyed. 57% rated it as one of the top three most challenging aspects of data preparation, a considerable increase from 41% in 2022.
This decline is particularly concerning given the rising stakes. Only 3% of business leaders believe their department has an acceptable level of data quality, while 87% of B2B sales professionals identify data accuracy as their top challenge. The gap between expectations and reality has never been wider.
Impact on Sales and Marketing Performance
Poor data quality creates measurable performance degradation across revenue teams. Sales representatives waste up to 27% of their time dealing with incorrect contact details instead of selling, creating a massive drain on productivity that compounds throughout the organization. Marketing teams face equally challenging impacts as targeting accuracy declines and campaign effectiveness suffers.
The ripple effects extend throughout the customer journey. Email marketing campaigns suffer when 40% of leads contain inaccurate data, leading to higher bounce rates and damaged sender reputation. Account-based marketing programs lose effectiveness when the targeting data is incomplete or outdated. Customer acquisition costs increase as teams chase unqualified leads and miss genuine opportunities due to incomplete prospect information.

What Poor Data Quality Really Costs Businesses
The true cost of poor data quality goes far beyond obvious metrics like bounced emails or failed calls. Research shows that poor data quality causes marketers to lose 21 cents from every dollar spent, creating substantial waste in marketing investments.
This translates to substantial losses. For example, a company spending $1 million annually on digital advertising effectively throws away $210,000 due to data quality issues.

While reputational damages are more difficult to measure, they can be just as damaging. Mailing to the wrong recipients, dialing contacts who have changed companies months before, or mispronouncing prospects’ names ruins brand image and shuts doors on high-value customers. In B2B economies where relationships generate revenue, such errors can ruin long-term possibilities.
The environment today for B2B data quality is challenging but not insurmountable. Companies that appreciate the magnitude of the problem and are prepared to put systematic solutions in place can make their data an asset, not a liability, and a competitive advantage, not a liability. The rest of this guide offers the frameworks, strategies, and best practices needed to make it a reality.
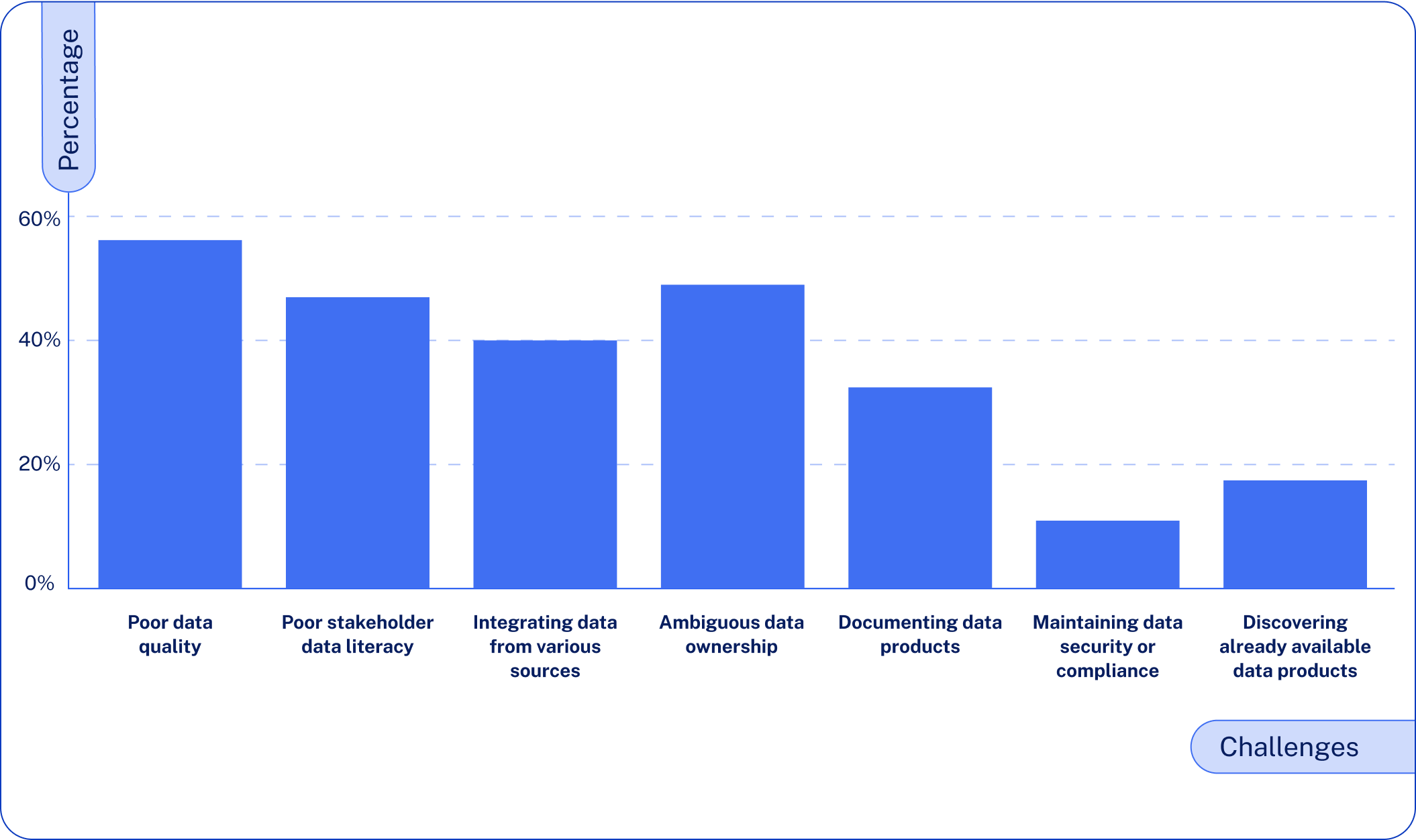
Most Common B2B Data Quality Issues
B2B businesses are faced with a complex web of data quality issues that undermine their marketing and sales effectiveness. From redundant records splitting up customer profiles to outdated data causing failed contact attempts, these issues add up over time to develop significant operational issues. Let’s examine the seven most critical data quality issues affecting B2B teams today and explore how they impact your bottom line.
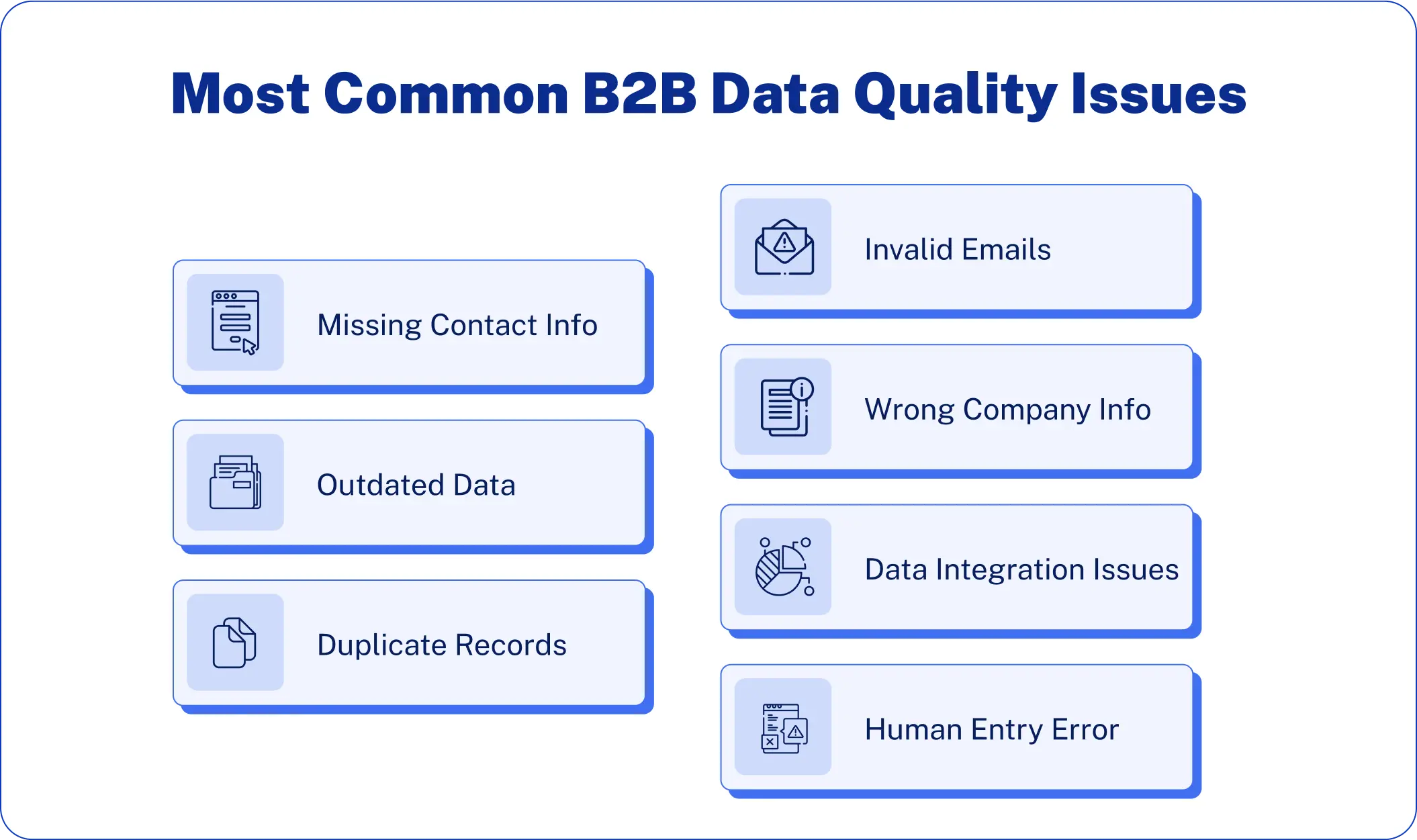
1. Incomplete contact information
Missing contact data is perhaps the most frustrating B2B sales and marketing problem. In the absence of critical fields like phone numbers, email addresses, job titles, or direct dial numbers, teams cannot effectively interact with prospects at the junctures of purchase or personalize outreach accordingly.
The impact of this incompleteness is immediate and measurable. Sales representatives waste valuable time researching basic information that should already exist in their systems. Marketing campaigns suffer from poor targeting when demographic or firmographic data is incomplete. Lead scoring becomes unreliable when key qualification criteria are missing from prospect records.
2. Outdated and stale data
Data decay affects every B2B database, with contact information becoming outdated at a rate of 2.1% per month. This means approximately 25% of your database records become inaccurate annually without active maintenance, creating a constant challenge for revenue teams.

People change jobs, receive promotions, switch companies, or update their contact preferences regularly. Company information evolves through mergers, acquisitions, rebranding initiatives, office relocations, and organizational restructuring. What was accurate when first collected can become completely wrong within months.
3. Duplicate records and data inconsistency
Duplicate records create fragmented understandings of customers and prospects, and this will take away from sales and marketing productivity. It is much more than a nuisance.
Duplicate records inflate database cost, skew analytics, and make accurate reporting an impossibility. Sales teams are perplexed by the history of interaction and buying signals when the same prospect is presented on multiple records. Marketing teams are baffled to score and nurture leads when prospect activity is fragmented across duplicates.
4. Invalid email addresses and bounced contacts
Email deliverability problems can trouble B2B marketing campaigns when databases contain inoperative, inactive, or incorrectly formatted email addresses. They damage sender reputation, reduce campaign performance, and waste marketing budget in contacting unreachable individuals.
Invalid email addresses are caused by a number of processes: typing mistakes in data entry, fictitious emails provided by leads to avoid follow-up, outdated addresses due to career change, and import formatting errors in the data. Each bounce message notifies email providers that your database health is poor, and this will affect deliverability for each subsequent campaign.
5. Inaccurate company information
B2B marketing and sales depend to a large extent on accurate firmographic data to find and prioritize accounts, personalize messaging, and discover buying opportunities. When firm data like revenue, employee count, industry vertical, or headquarters is inaccurate, teams make strategic decisions from the wrong assumptions.
Inaccurate revenue data produces misaligned pricing strategies and misguided sales strategies. Inaccurate counts of employees impact territory mapping and resource planning. Incorrect industry classifications lead to the wrong messaging and missed market opportunities. Outdated company addresses create problems for field sales professionals and direct mail marketing.
6. Data integration problems
Modern B2B businesses operate a number of systems including CRM applications, marketing automation systems, customer success tools, and business intelligence reporting dashboards, each of these tools containing overlapping but potentially contradictory data. These system silos create fundamental data quality problems that affect every aspect of revenue operations.
Integration problems may arise during system migrations, acquisitions, or technology refreshes. Companies frequently discover that data formats, field structures, and validation rules differ significantly between platforms, and clean data transfer is all but impossible without large-scale cleansing and standardization efforts.
7. Human error in data entry
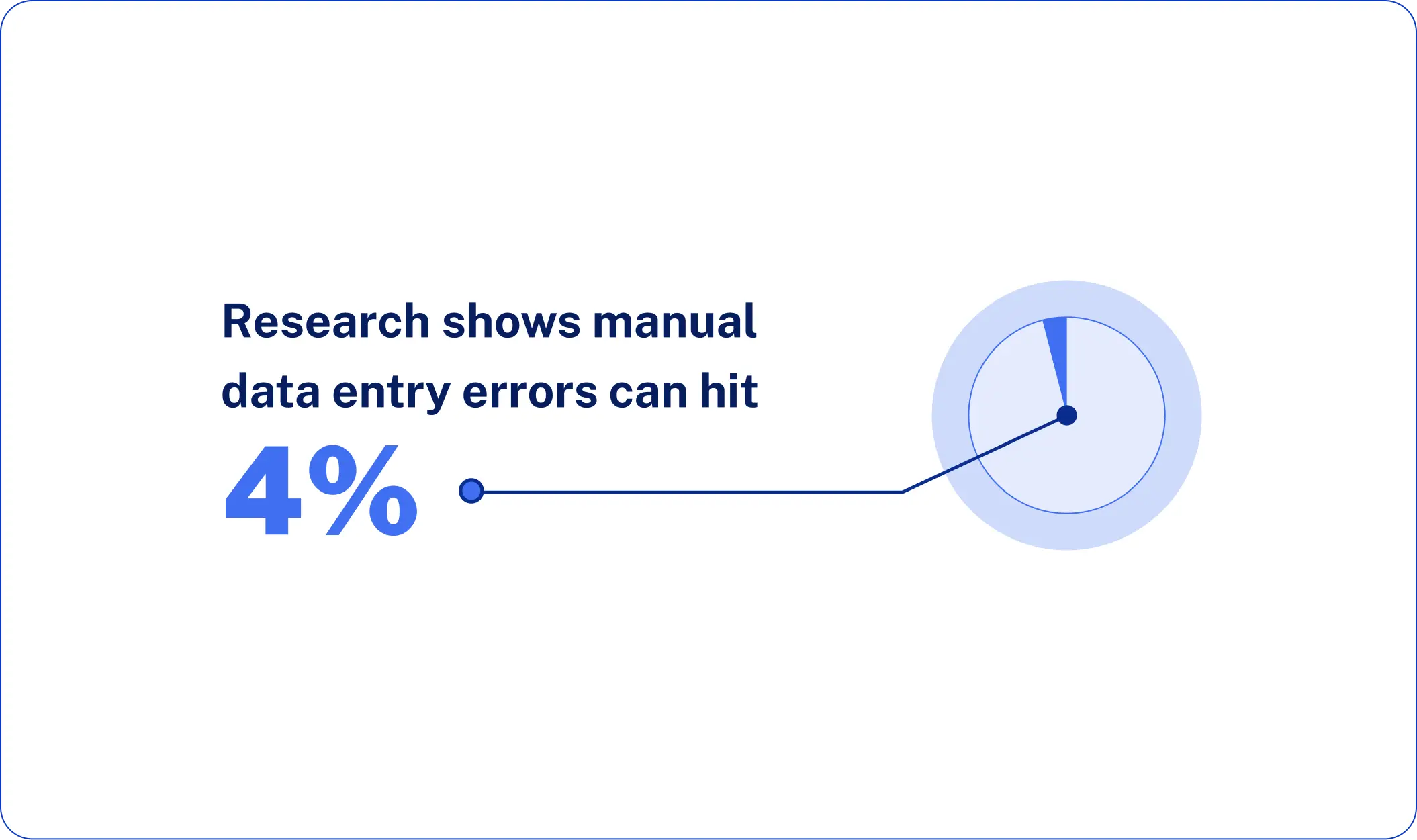
Common human errors include misspelled names that damage professional credibility, incorrect email addresses with transposed letters that cause bounces, wrong phone numbers with digit errors that waste sales time, and inaccurate company information that affects targeting and segmentation. Research shows that human error rates in manual data entry can be as high as 4%, meaning 4 mistakes for every 100 entries.
The issue worsens when organizations lack standardized data entry procedures, validation rules, or quality control processes. Without established standards on the way data should be formatted and entered, teams develop inconsistent procedures that lead to long-term data quality issues across different departments and campaigns.
Why B2B Data Quality Problems Occur?
Learning the fundamentals of B2B data quality issues is critical to the construction of efficient prevention measures. They don’t crop up at random; they are a result of certain organizational, technical, and human factors that accumulate over time.
The modern B2B market shifts at a historic rate, with companies consolidating, renaming themselves, and reorganizing often, and professionals changing jobs more regularly than the previous generation. Organizations are unable to keep up with the natural evolution of their target markets and customer bases.
B2B organizations collect information from a multitude of sources, including web forms, trade shows, purchased lists, and sales contacts, each with diverse levels of quality and formatting standards. Without models of centralized governance or standard processes in place, teams develop irregular practices that create quality issues from the moment data enters systems. Limitations of older technology, inefficient system integration, and behavior-oriented factors like pressure for speed and lack of training fuel these problems and make manual data administration highly susceptible to error in advanced B2B environments.
Proven Strategies for B2B Data Quality Management
Effective B2B data quality management results from systematic solutions for prevention and remediation. Businesses that implement full data quality solutions enjoy concrete improvements in campaign outcomes, sales performance, and revenue growth. The following established techniques provide a path to transforming your data from liability to a competitive edge.

1. Data Governance Framework
Developing a robust data governance framework is the foundation of sustained data quality management. It defines roles, responsibilities, standards, and processes for the consistent handling of data across your organization.
Approach: Create a three-pillar framework that states who manages data, what standards they work to, and how success is measured. Start by assigning data stewards to their own major domains, like contacts and accounts. Research shows that companies with dedicated data management leaders have 42% more confidence in data quality. Define comprehensive data standards covering formats, required fields, and validation rules, and then put KPIs in place to monitor completion rates, accuracy scores, and duplication percentages. This creates accountability through measurable outcomes tied to business value.
2. Data Validation and Verification
Proactive verification stops low-quality data from entering your systems, and verification processes detect and correct issues with existing records.
Approach: Apply validation rules at every data entry point with real-time phone number formatting, company name normalization, and email syntax validation. Utilize progressive profiling to collect data in small increments rather than bombarding prospects with lengthy forms, preventing abandonment in building complete profiles. Integrate third-party verification services that check email addresses, phone numbers, and company data automatically against authoritative sources.
3. Data Validation and Verification
Preventive validation prevents poor-quality data from entering your systems, while verification procedures catch up with and repair defects in existing records.
Approach: Take advantage of validation controls at every data entry point with real-time email syntax verification, phone number formatting, and company name standardization. Apply progressive profiling to collect data in phases rather than inundating prospects with lengthy forms, reducing abandonment rates while filling out complete profiles. Add third-party verification services to automatically verify email addresses, phone numbers, and company data against authoritative sources in real time, catching 60-80% of common data entry mistakes before they impact business processes.
4. Data Enrichment and Enhancement
Systematic enrichment of information transforms sparse records into voluminous prospect profiles that support more effective sales and marketing campaigns.
Approach: Leverage automated data appending features to fill out blank fields with available data points as match keys with external databases. Integrate social media and web intelligence sources like LinkedIn and corporate websites to capture real-time job changes, company announcements, and professional transitions. Layer buyer intent data to identify prospects actively looking for solutions, enabling prioritized contact based on interest signals expressed rather than static demographic definitions.
5. Duplicate Detection and Management
Good duplicate management is a mixture of prevention and measured cleanup processes to maintain consistent customer views.
Approach: Use fuzzy match rules that identify likely duplicates despite the differences in spelling, format, or completeness. Example is “IBM”, “International Business Machines”, and “I.B.M. Corp” refer to the same entity.
Research shows that 15% of leads contain duplicate records, making systematic deduplication essential for maintaining accurate customer views and preventing fragmented prospect relationships. Establish merge and purge procedures that preserve maximum information while maintaining activity history. Start prevention controls with company domain match and other qualifiers to automatically match new contacts with already existing accounts in order to avoid duplicates at the source.

6. Automated Data Hygiene
Regular automated maintenance operations keep databases clean and current without requiring constant human intervention.
Approach: Perform regular automated quality audits that verify for incomplete data, formatting issues, and probable duplicates. Perform regular email validity checking that watches for high bounces, unengaged address lists, and flags deliverability concerns to protect sender reputation. Employ data decay monitoring that identifies records past due for update, particularly contact details susceptible to a high frequency of change, triggering automated verification processes for high-value leads.
7. Integration and System Alignment
Offering data consistency throughout systems prevents quality issues caused by poor integration and data silos.
Approach: Establish master data management with single sources of truth for key entities, leveraging real-time API integrations in place of error-prone batch exports and imports. Map data flows between systems to find points of potential failure and sources of degradation in quality. Create synchronization processes that maintain relationships between data across CRM, marketing automation, and other systems, with immediate updates propagating consistently throughout the technology stack.
8. Training and Change Management
Human factors remain critical to data quality success, making training and change management essential components of any comprehensive strategy.
Approach: Deliver role-specific training tailored to different data responsibilities, sales teams learn contact entry procedures, while marketing teams focus on list management and segmentation practices. Foster quality culture by incorporating data metrics into performance evaluations and recognition programs, making data stewardship part of job expectations. Provide continuous education on new data sources, validation tools, and evolving best practices through regular training sessions and documentation updates.
9. Technology Stack Optimization
The right technology backbone supports all the other data quality initiatives while automating common maintenance tasks.
Approach: Invest in specialized data quality platforms that have strong cleaning, validation, and monitoring features that extend beyond the baseline CRM functionality. Leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning for predictive data quality, auto-matching, and smart enrichment that identifies patterns that human reviewers may miss. Employ integration platforms with built-in data quality capabilities that maintain cleanliness as data moves across systems and applications.
10. Measuring Success and ROI
Measurement of business ROI from data quality improvement justifies spending and guides future optimization efforts.
Approach: Track campaign performance improvements like email deliverability boosts, lead conversion rate increase, and total campaign ROI gains—typically seeing 15-30% performance increase with better data quality. Track sales efficiency measures like reduced research time, better successful contact attempts, and better lead qualification accuracy, typically seeing a 20-40% productivity gain. Calculate overall cost savings resulting from reduced manual cleaning, fewer campaign failures, and improved operating efficiency, with organizations typically realizing 300-500% ROI in the first year of overall data quality initiatives.
Essential Tools and Technologies For Managing B2B Data Quality
The modern B2B data quality landscape offers an integrated ecosystem of technologies and tools designed to address every stage of data management. From basic validation through advanced AI-infused enrichment, the right selection of technologies can radically improve your data quality outcomes and reduce manual effort and operational costs.
-
AI Ark
AI Ark builds artificial intelligence into its core from the start instead of tacking it onto existing data platforms later. Embedding AI deep in the system allows it to collect, analyze, normalize, and huddle data, updating every 30 days to stay relevant. Once you put AI Ark’s Lookalike Search to work looking for prospects that are similar to your best customers, you can use the company’s specific technology, domain, and intent information to run much more targeted campaigns.
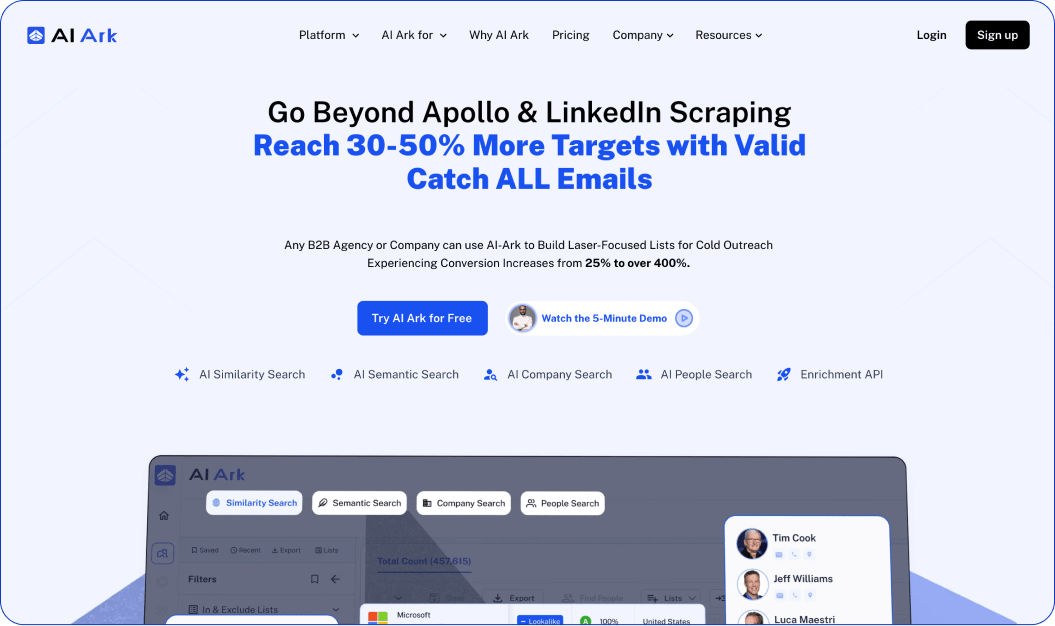
Key Capabilities:
- AI-powered data discovery and segmentation with precise insights
- Sophisticated B2B database with cleansed emails and social media insights
- Company change notifications and market movement alerts in real-time
- Slender competitor analysis and technographic intelligence
- GDPR-compliant data handling with enterprise-level security
- Seamless integration opportunities for current tech stacks
Best For: Companies seeking AI-powered data quality with predictive insights and automated enrichment capabilities. Particularly beneficial for companies that require sophisticated segmentation and competitive intelligence.
-
ZoomInfo
ZoomInfo provides access to one of the largest and most validated B2B databases in the world, leveraging web crawling, data partnerships, human intelligence collection, and AI/ML validation to guarantee that it’s accurate. Use ZoomInfo’s multi-product suite, consisting of SalesOS for prospecting, MarketingOS for account-based marketing, and OperationsOS for managing data. The suite is optimized to deliver firmographic, technographic, and intent data to power enterprise business operations.
Key Capabilities:
- Large database comprising complete company and contact information
- Advanced intent signals and buying behavior analytics
- Detailed CRM integrations (Salesforce, HubSpot, Microsoft Dynamics)
- Chrome extension for seamless prospecting on all platforms
- Custom pricing and enterprise features
- DNC list scrubbing in several countries
Best For: Large enterprises and established organizations requiring extensive data coverage, detailed integrations, and high-end analytics features. Ideal for companies with big budgets and multidimensional go-to-market strategies.
-
Apollo.io
Apollo.io provides access to over 275 million contacts across 73 million companies with integrated sales engagement features. Leverage Apollo’s prospecting functions with 65+ filters for focused targeting, with automated email sequences, call logging, and integration with LinkedIn for do-it-all outreach campaigns. The platform centers on data visibility and user feedback to maintain quality standards.
Key Capabilities:
- Big verified contact database (275M+ contacts)
- Integrated email sequencing and sales automation
- LinkedIn and website prospecting Chrome extension
- Real-time email verification and deliverability tracking
- Native CRM integrations with transparent pricing
- Core features included in the free plan
Best For: Small to medium-sized businesses and startups who require an affordable all-in-one solution for prospecting and outreach. Ideal for teams requiring both data access and engagement tools in one platform.
-
Salesforce
Leverage the integrated data quality functionalities in Salesforce, like duplicate management, validation rules, and automatic enrichment services. Take advantage of Einstein Data for capabilities like smart matching, data completion, and quality scoring directly integrated into your existing Salesforce environment. Tap into the crowd-sourced validation mechanism of Data.com, supplemented with third-party providers of data to achieve accuracy without leaving your CRM.
Key Capabilities:
- Integrated within the CRM with no setup required
- Automated duplicate identification and recommended merge
- Real-time validation rules and data normalization
- Einstein data quality scoring through AI
- Data maintenance workflow automation
- Seamless integration with the entire Salesforce ecosystem
Best For: Organizations already on Salesforce CRM who want to maintain data quality easy without added tool complexity. Ideal for companies seeking tight integration of data quality with existing sales processes.
-
HubSpot Operations Hub
HubSpot’s Operations Hub allows for a unified and shared data strategy with the ability to sync data, monitor quality, and automate cleaning workflows all at once. You can utilize custom properties, calculated properties, and data quality automation with shared data strategies that cover all of HubSpot’s marketing, sales, and service hubs. You can also use the HubSpot workflow engine to automate the tracking, cleaning, and enrichment of data with custom business rules and logic to trigger the auto-flagging and cleaning of data.
Key Capabilities:
- Data syncing across multiple systems and platforms
- Customizable data quality automation processes/workflows
- Calculated properties and formatting for data quality
- Auto data monitoring with real-time data and dashboards for quality
- Progressive profiling and optimizing for forms
- Native integration with all of HubSpot’s platform suite
Best For: Mid-market companies using HubSpot’s ecosystem who need comprehensive data operations capabilities. Perfect for organizations requiring custom data workflows and cross-platform synchronization.
Best Practices for Different Business Functions
B2B data quality requirements vary immensely across diverse business functions with dissimilar workflows, success criteria, and stakeholder expectations. What may work for the sales team might not work for marketing operations, and finance teams have entire different data quality priorities than customer success teams. Understanding these function-driven needs is essential to implement strategic data quality best practices that can demonstrate value to each functional area.
Sales Teams: Maximizing Contact Success
Primary Data Quality Focus: Accurate contact information, current job titles, and verified company details that enable successful outreach and relationship building.
Core Practices:

Real-Time Contact Validation: Leverage automated email and phone verification when contacts enter. Sales representatives spend up to 27% of their time scrubbing bad contact data, so validation is key to staying productive. Utilize software that tests email deliverability, validates phone number format, and flags potentially stale data before attempting outreach.
Region and Account Alignment: Establish precise data standards for geographic markets, company hierarchies, and account ownership. Use standardized industry classifications, revenue ranges, and employee count ranges to ensure consistent territory management and prevent account conflict between team members.
Opportunity Data Hygiene: Keep opportunity records up-to-date with consistent stage names, the same date formatting, and accurate amounts. Use validation rules requiring certain fields at each step in sales and automatically flag opportunities not updated after a certain period.
Lead Scoring and Qualification: Employ standard lead scoring policies using confirmed firmographic and demographic data. Standardize job titles, company sizes, and industry classifications to ensure adequate lead qualification and routing. Misrecorded data can lead to qualified leads being routed improperly to various team members or misclassification altogether.
Activity Tracking Standards: Enforce standard data entry practices around sales activities, including the recording of call outcomes, email replies, and meeting notes. This will lead to acceptable pipeline forecasting and allow coaching effectiveness to be based on good activity metrics.
Marketing Teams: Campaign Accuracy
Primary Data Quality Focus: Accuracy of segmentation, deliverability of email, and complete prospect files for personal, targeted campaigns.
Core Practices:

Segmentation and Personalization: Maintain in-depth and current demographic, firmographic, and behavioral data to enable precise audience segmentation. Employ progressive profiling methods that collect additional data points stepwise without overwhelming prospects, building rich profiles over multiple touchpoints.
Email Deliverability Management: Utilize strong email hygiene solutions with real-time validation, bounce management, and suppression list management. Poor quality of email data causes marketers to spend 21 cents for every media dollar wasted, and therefore, render deliverability protection vital to the ROI of campaigns.
Campaign Attribution and Tracking: Using UTM parameters for normal application, lead source tracking, and campaign tagging across all positions of advertising. Standardize naming conventions across campaigns, content assets, and lead sources so attribution analysis is dynamic and you can measure ROI.
Lead Lifecycle Management: Establish authoritative lead status definitions and automated steps to update prospect records based on engagement activity. Implement data quality validation that prevents leads from becoming pipeline-stuck due to incomplete or invalid information.
Account-Based Marketing Data: Maintain unified account details that consolidate all contacts for a target company. Companies should be named consistently, the organizational structure should be accurate, and the stakeholder information should be kept up to date so ABM campaigns and account penetration efforts can be effective.
Customer Success: Retention Through Data-Driven Insights
Primary Data Quality Focus: Complete Customer Profiles, Usage Data Accuracy, and Health Score Trustworthiness that provide you the ability to retain and expand proactively.
Core Practices:

Customer Monitoring: Leverage detailed data collection on product utilization, support ticket history, and engagement metrics. Confirm data accuracy across all customer touchpoints to enable precise health scoring and early warning systems for identifying churn risk.
Opportunity Expansion Identification: Maintain current organizational charts, decision-maker contact information, and active contract data to identify opportunities for cross-selling and upselling. Track the growth of customer organizations, new stakeholders, and shifting business needs through periodic data refreshes.
Support Case Management: Implement standardized data entry procedures for support cases, like accurate classification of problems, tracking of resolution history, and collection of customer feedback. This enables trend discovery, knowledge base improvement, and preventive issue avoidance.
Renewal Planning: Maintain up-to-date contract details, pivotal contacts for vital stakeholders, and usage data in order to allow renewal conversations. Grant customer success teams visibility into total, correct information about customer value achievement and business outcomes.
Customer Advocacy Programs: Track customer satisfaction scores, willingness to recommend, and success story qualification via analytical data collection and analysis. Maintain accurate records of customer success and business outcomes for use in case study development and advocacy program administration.
Your Roadmap to Data-Driven B2B Success With AI Ark
Throughout this guide, we’ve outlined the critical importance of B2B data quality, set forth typical issues, and explained proven processes for transformation. Let’s now take a look at how these concepts come together in practice through the integrated approach to B2B data quality management by AI Ark.
Will you be the business that captures tomorrow’s prospects today, or will you still be chasing yesterday’s leads as your competition closes the deals you should have won?
The tactics are effective. The technology is available. Your ROI is quantifiable. Your data-driven B2B success story begins with your next choice.
Contact us today and learn how AI Ark’s AI-powered platform can accelerate your deployment of the strategies detailed in this guide.